- 您现在的位置:买卖IC网 > Sheet目录3854 > PIC18F4450-I/PT (Microchip Technology)IC PIC MCU FLASH 8KX16 44TQFP
155
XMEGA A [MANUAL]
8077I–AVR–11/2012
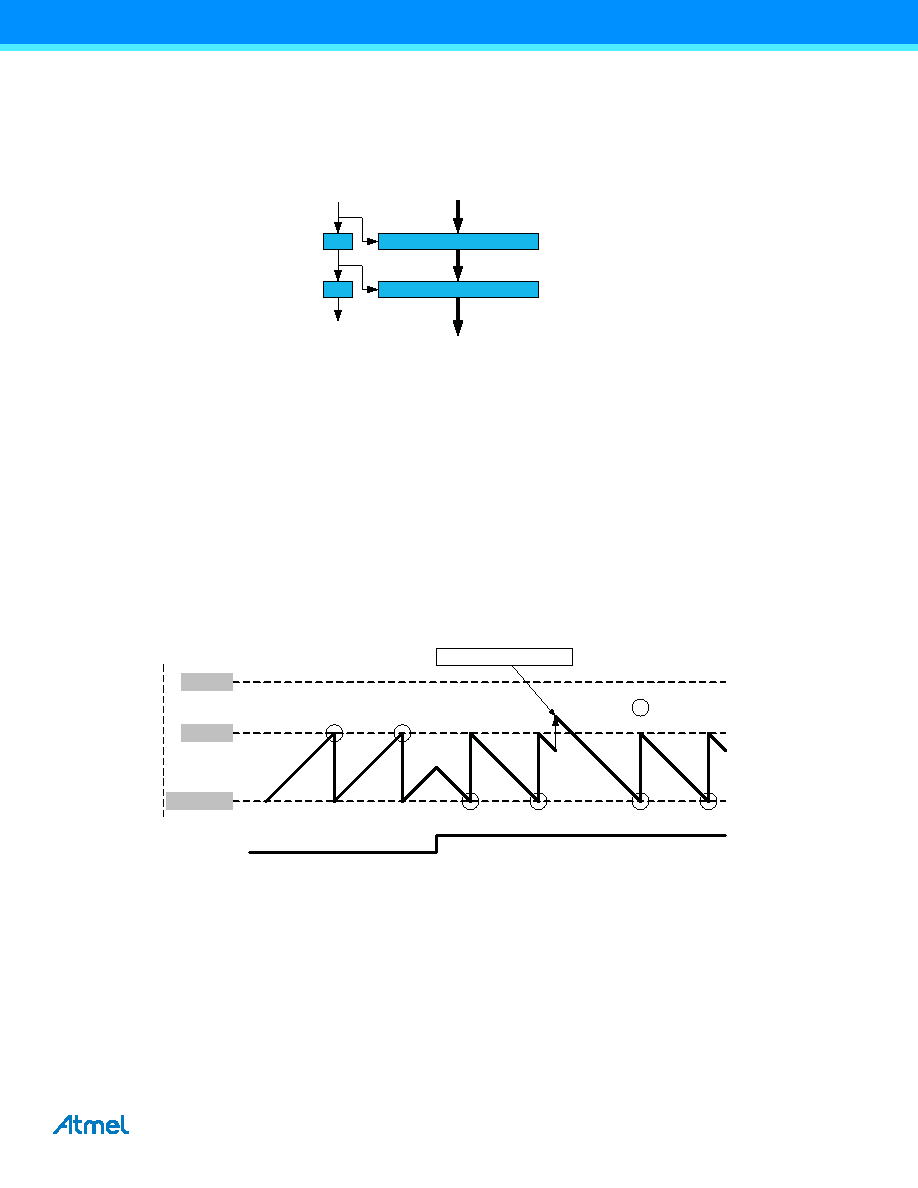
corresponding CCx register act like a FIFO. When the CC register is empty or read, any content in the buffer register is
passed to the CC register. The buffer valid flag is passed to set the CCx interrupt flag (IF) and generate the optional
interrupt.
Figure 14-5. Capture double buffering.
Both the CCx and CCxBUF registers are available as an I/O register. This allows initialization and bypassing of the buffer
register and the double buffering function.
14.6
Counter Operation
Depending on the mode of operation, the counter is cleared, reloaded, incremented, or decremented at each
timer/counter clock input.
14.6.1 Normal Operation
In normal operation, the counter will count in the direction set by the direction (DIR) bit for each clock until it reaches TOP
or BOTTOM. When up-counting and TOP is reached, the counter will be set to zero when the next clock is given. When
down-counting, the counter is reloaded with the period register value when BOTTOM is reached.
Figure 14-6. Normal operation.
As shown in Figure 14-6, it is possible to change the counter value when the counter is running. The write access has
higher priority than count, clear, or reload, and will be immediate. The direction of the counter can also be changed
during normal operation.
Normal operation must be used when using the counter as timer base for the capture channels.
14.6.2 Event Action Controlled Operation
The event selection and event action settings can be used to control the counter from the event system. For the counter,
the following event actions can be selected:
Event system controlled up/down counting
BV
"capture"
IF
CNT
CCxBUF
CCx
EN
"INT/DMA
request"
data read
CNT
BOTTOM
MAX
"update"
TOP
CNT written
DIR
发布紧急采购,3分钟左右您将得到回复。
相关PDF资料
21FMN-BMTTR-A-TB
CONN FMN HSNG 21POS STAG REV SMD
PIC16LF87-I/ML
IC MCU FLASH 4KX14 EEPROM 28QFN
PIC24HJ32GP204-I/PT
IC PIC MCU FLASH 32K 44TQFP
20FMN-BMTTR-A-TB
CONN FMN HSNG 20POS STAG REV SMD
PIC16F88-I/SS
IC MCU FLASH 4KX14 EEPROM 20SSOP
18FMN-BMTTR-A-TB
CONN FMN HSNG 18POS STAG REV SMD
17FMN-BMTTR-A-TB
CONN FMN HSNG 17POS STAG REV SMD
PIC18LF46J11-I/ML
IC PIC MCU FLASH 64K 2V 44-QFN
相关代理商/技术参数
PIC18F4450T-I/ML
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 16KB FL 768 RAM 34 I/O FS-USB 2.0 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4450T-I/PT
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 16KB FL 768 RAM 34 I/O FS-USB 2.0 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4455-BL
制造商:POWERLITE SYSTEMS 功能描述:PIC18F445 W/ BOOTLOADER FOR FLASHLAB 制造商:POWERLITE SYSTEMS 功能描述:PIC18F445 W/ BOOTLOADER, FOR FLASHLAB 制造商:POWERLITE SYSTEMS 功能描述:PIC18F445 W/ BOOTLOADER, FOR FLASHLAB; Silicon Manufacturer:Powerlite Systems; Core Architecture:PIC; Kit Contents:Board; Features:Bootloader Programming, RS232 Connector for Boot-Loading and Serial Comms ;RoHS Compliant: Yes
PIC18F4455-I/ML
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 24kBF 2048RM FSUSB2 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4455-I/P
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 24kBF 2048RM FSUSB2 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4455-I/PT
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 24kBF 2048RM FSUSB2 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4455T-I/ML
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 24kBF 2048RM FSUSB2 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT
PIC18F4455T-I/PT
功能描述:8位微控制器 -MCU 24kBF 2048RM FSUSB2 RoHS:否 制造商:Silicon Labs 核心:8051 处理器系列:C8051F39x 数据总线宽度:8 bit 最大时钟频率:50 MHz 程序存储器大小:16 KB 数据 RAM 大小:1 KB 片上 ADC:Yes 工作电源电压:1.8 V to 3.6 V 工作温度范围:- 40 C to + 105 C 封装 / 箱体:QFN-20 安装风格:SMD/SMT